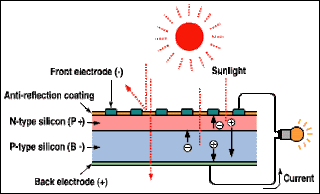
A solar cell is a kind of semiconductor device that takes advantage of the photo-voltaic effect, in which electricity is produced when the semiconductor's PN junction is irradiated. When light strikes a solar cell, part of it is reflected, part of it is absorbed, and part of it passes through the cell.
The absorbed light excites the bound electrons into a higher energy state, making them free electrons. These free electrons move about in all directions within the crystal, leaving holes where the electrons used to be, and the holes also shift around the crystal. The electrons (-) collect in the N-layer, the holes (+) in the P-layer. When the outside circuit is closed, electricity flows.
Solar photovoltaic(Solar electrical panels) -
Advantages-
Sustainable It is a well proven technology. Well suited to providing power in home or single building applications. Meets peak demand.
Disadvantages-
While the panels are environmentally benign once they are built, the manufacturing process requires large amounts of energy.
One less common, expensive, but highly efficient type of solar panel, gallium arsenide, contains toxins that need to be disposed of carefully at the end of the life of the panel.
Solar energy is spread relatively thinly. If a photovoltaic generator is to produce much electricity it has to cover a large area. However, in the case of home electrical supplies the roof provides sufficient available space.
Does not produce much power when the sun isn't shining, and negligible power at night. An alternative power supply is needed for these periods.
Electricity generated by solar panels is quite expensive.
A solar photovoltaic panel must operate for a considerable time before it produces more power than was required in its manufacture. The US National Renewable Energy Labaratory states on its energy payback page that "Paybacks for multicrystalline modules are 4 years for systems using recent technology and 2 years for anticipated technology. For thin-film modules, paybacks are 3 years using recent technology, and just 1 year for anticipated thin-film technology".
Can be combined with small-scale wind-generated electricity or with mains power. Alternatively, batteries can be charged when more electricity is being generated than is being consumed. Excess electricity can be sold to the grid in some cases.
In the past photovoltaic panels have predominantly been based on silicon. It is possible that in future a larger proportion will use alternatives such as gallium arsenide (GaAs) or copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). While these elements are much rarer than silicon, they can be used as a thin film; this makes the cost competative. One wonders if there pollution implications in their eventual disposal.
http://www.geocities.com/daveclarkecb/ElecGenProsCons.html#Solar%20photovoltaicMaybe someone can post some stats on the cost or the growth of the solar industry and electric genration over the past 40 years.
No comments:
Post a Comment